Hello World
While you can immediately begin to analyze your data using Heavy Immerse, you might choose to create your own interface and custom charts.
This topic demonstrates how you can:
Clone the mapd-connector repository.
Connect to a HEAVY.AI server instance.
Retrieve the results of a SQL query.
Display the results on an HTML page.
Clone
Much of the underlying infrastructure you need to interact with a HEAVY.AI server is provided by the mapd-connector repository. You can clone the repository locally to take advantage of its utilities.
To clone the mapd-connector repository:
Click Clone or Download.
Choose whether to clone the repository using HTTPS or SSH, or optionally download a Zip archive to expand on your local drive.
For more information on cloning GitHub repositories, see https://help.github.com/articles/cloning-a-repository/
Open mapd-connector/examples/browser.html in a web browser to connect to a sample HEAVY.AI server instance and display information from the sample database. You can open mapd-connector/examples/browser.js in a text editor and follow along as the following sections describe how the script connects, retrieves, and displays data from the HEAVY.AI server.
Connect
The lynchpin of the application is establishing a connection to HEAVY.AI. Fortunately, the MapdCon object does the heavy lifting for you. You provide the location and port of the HEAVY.AI host and your user credentials to create a connection.
const connector = new window.MapdCon()
connector
.protocol("https")
.host("metis.mapd.com")
.port("443")
.dbName("heavyai")
.user("admin")
.password("HyperInteractive")
.connectAsync()
Retrieve
Connecting to the HEAVY.AI server is not the final goal, of course. Once you have a connection, you can send SQL queries to retrieve data.
First, create constant variables for your SQL queries.
// The total number of tweets from Columbia
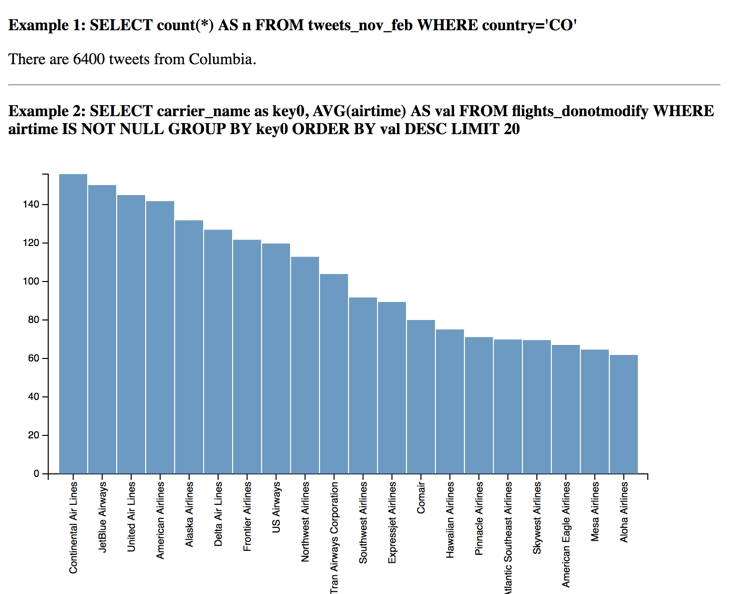
const query = "SELECT count(*) AS n FROM tweets_nov_feb WHERE country='CO'"
// try changing airtime to arrdelay in the query
const query2 =
"SELECT carrier_name as key0, AVG(airtime) AS val FROM flights_donotmodify WHERE airtime IS NOT NULL GROUP BY key0 ORDER BY val DESC LIMIT 100"Create an empty array for your query options.
const defaultQueryOptions = {}Connect as shown above.
const connector = new window.MapdCon()
connector
.protocol("https")
.host("metis.mapd.com")
.port("443")
.dbName("heavyai")
.user("admin")
.password("HyperInteractive")
.connectAsync()Use a promise to send a series of queries, including the ones defined as constants.
.then(session =>
// now that we have a session open we can make some db calls:
Promise.all([
session.getTablesAsync(),
session.getFieldsAsync("flights_donotmodify"),
session.queryAsync(query, defaultQueryOptions),
session.queryAsync(query2, defaultQueryOptions)
])
)Display
Promise returns a values object with an array of query results. The first item in the values array is a list of tables. Write the results to the browser console.
.then(values => {
console.log(
"All tables available at metis.mapd.com:",
values[0].map(x => x.name)
)The second item in the array contains a list of fields in the table flights_donotmodify.
// handle result of getFieldsAsync
console.log(
"All fields for 'flights_donotmodify':",
values[1].reduce((o, x) => Object.assign(o, { [x.name]: x }), {})
)The third query contains a count of Twitter™ tweets from Columbia. Display that in the HTML page using the DOM.
// handle result of first query
document.getElementById("result-async").innerHTML =
"There are " + values[2][0].n + " tweets from Columbia."
console.log("Query 1 results:", Number(values[2][0].n))The final query returns the average air time for flights listed in the flights_donotmodify table, with a limit of 100 records. Display the results as a chart using the createRowChart method.
// handle result of 2nd query
createRowChart(values[3])
console.log(
"Query 2 results:",
values[3].reduce((o, x) => Object.assign(o, { [x.key0]: x.val }), {})
)
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Something bad happened: ", error)
})Use the array to create a chart using the D3 API. This example is based on an example from the free ebook D3 Tips and Tricks
function createRowChart(data) {
var margin = { top: 20, right: 20, bottom: 150, left: 40 },
width = 600
height = 300
var x = d3.scale.ordinal().rangeRoundBands([0, width], 0.05)
var y = d3.scale.linear().range([height, 0])
var xAxis = d3.svg
.axis()
.scale(x)
.orient("bottom")
.tickFormat(function(d, i) {
return d
})
var yAxis = d3.svg
.axis()
.scale(y)
.orient("left")
.ticks(10)
var svg = d3
.select("#chart")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", width + margin.left + margin.right)
.attr("height", height + margin.top + margin.bottom)
.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(" + margin.left + "," + margin.top + ")")
x.domain(
data.map(function(d) {
return d.key0
})
)
y.domain([
0,
d3.max(data, function(d) {
return d.val
})
])
svg
.append("g")
.attr("class", "x axis")
.attr("transform", "translate(0," + height + ")")
.call(xAxis)
.selectAll("text")
.style("text-anchor", "end")
.attr("dx", "-.8em")
.attr("dy", "-.55em")
.attr("transform", "rotate(-90)")
svg
.append("g")
.attr("class", "y axis")
.call(yAxis)
.append("text")
.attr("transform", "rotate(-90)")
.attr("y", 6)
.attr("dy", ".71em")
.style("text-anchor", "end")
svg
.selectAll("bar")
.data(data)
.enter()
.append("rect")
.style("fill", "steelblue")
.attr("x", function(d) {
return x(d.key0)
})
.attr("width", x.rangeBand())
.attr("y", function(d) {
return y(d.val)
})
.attr("height", function(d) {
return height - y(d.val)
})
}