Linemap
To learn more about linemap charts and how to create one, please view this video.
The Linemap superimposes LINESTRING or MULTILINESTRING objects onto a geographic map. Uses include tracking shipping and transportation routes in real time, and studying geographic features such as fault lines.
Features
Quantity
Notes
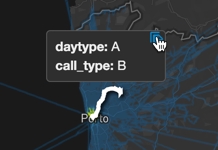
Chart Popup Information
When you hover over a Linemap chart, a popup box appears that contains the column information for the highlighted area. You can copy this information to the clipboard. If the column information includes a URL, you can click the URL to open it in a browser.
Examples
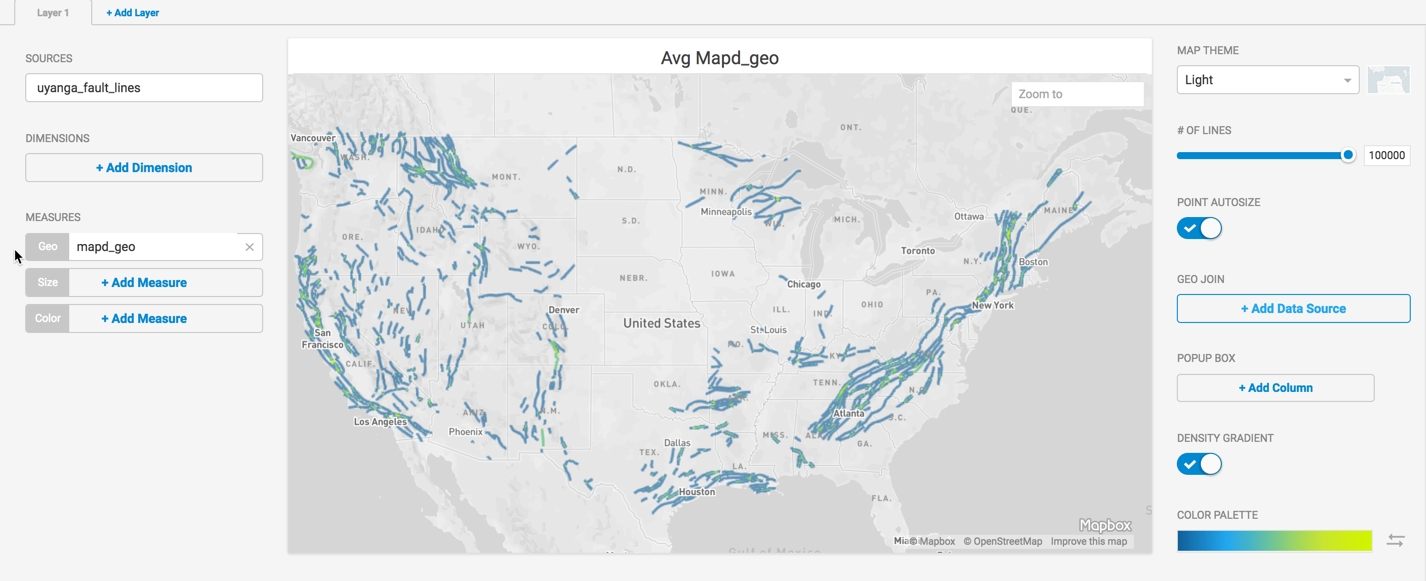
This example uses a dataset that maps geological fault lines in the United States of America, similar to datasets available at the Koordinates.com site. Set the Geo field to mapd_geo.
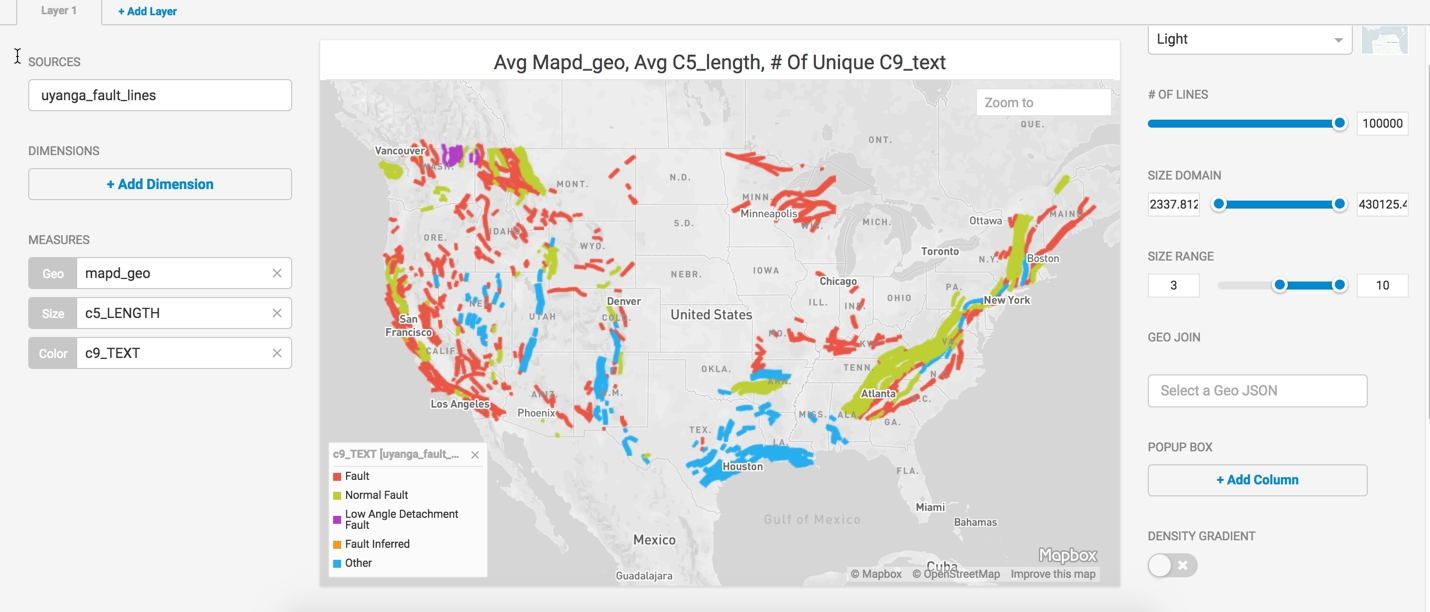
You can use length to determine the width of the lines to make longer faults stand out. You can also use a text label for the color, which provides a legend and a guide to the type of faults displayed.
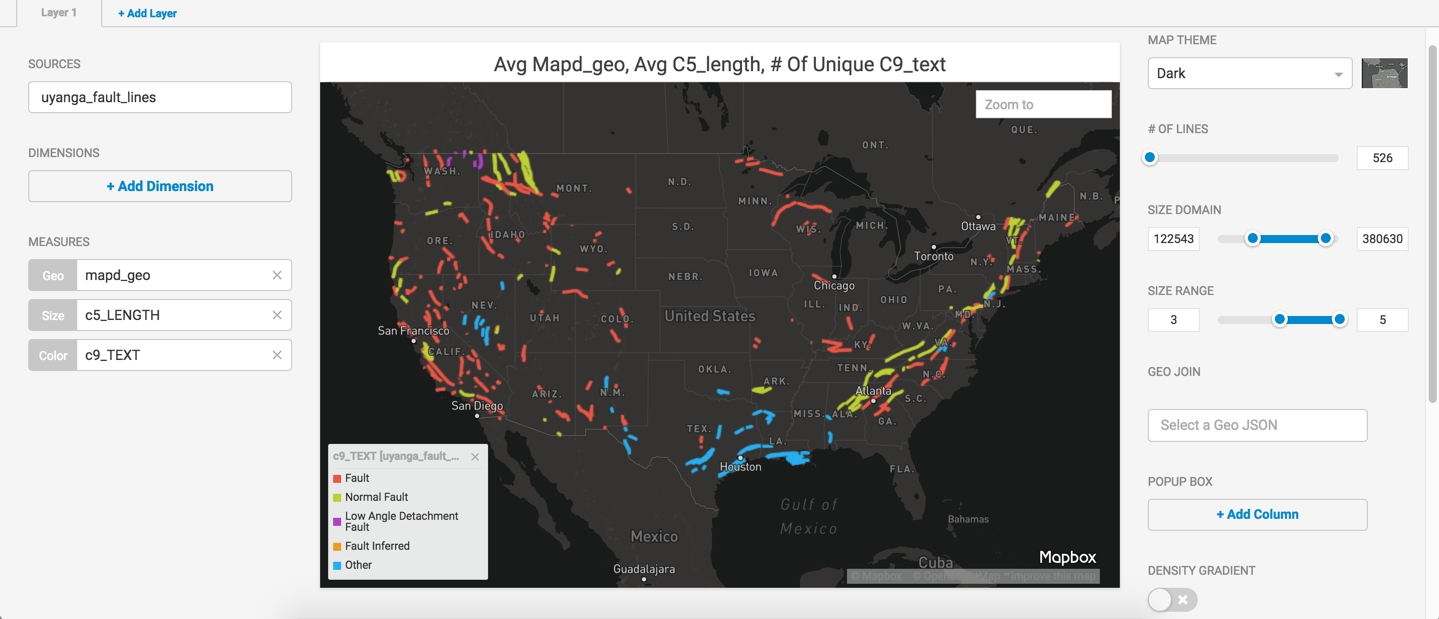
You can fine tune the graph further with enhancements such as changing the map theme, reducing the number of lines, changing the size domain and range, and adding values to the pop-up box.
Loading Linestring Data for Linemap
You can load your own linestring data to create Linemap charts. Linestring coordinates must be:
Expressed as longitude latitude
Between -180 to 180 (longitude), -90 to 90 (latitude)
North and East coordinates are positive numbers, South and West are negative numbers.
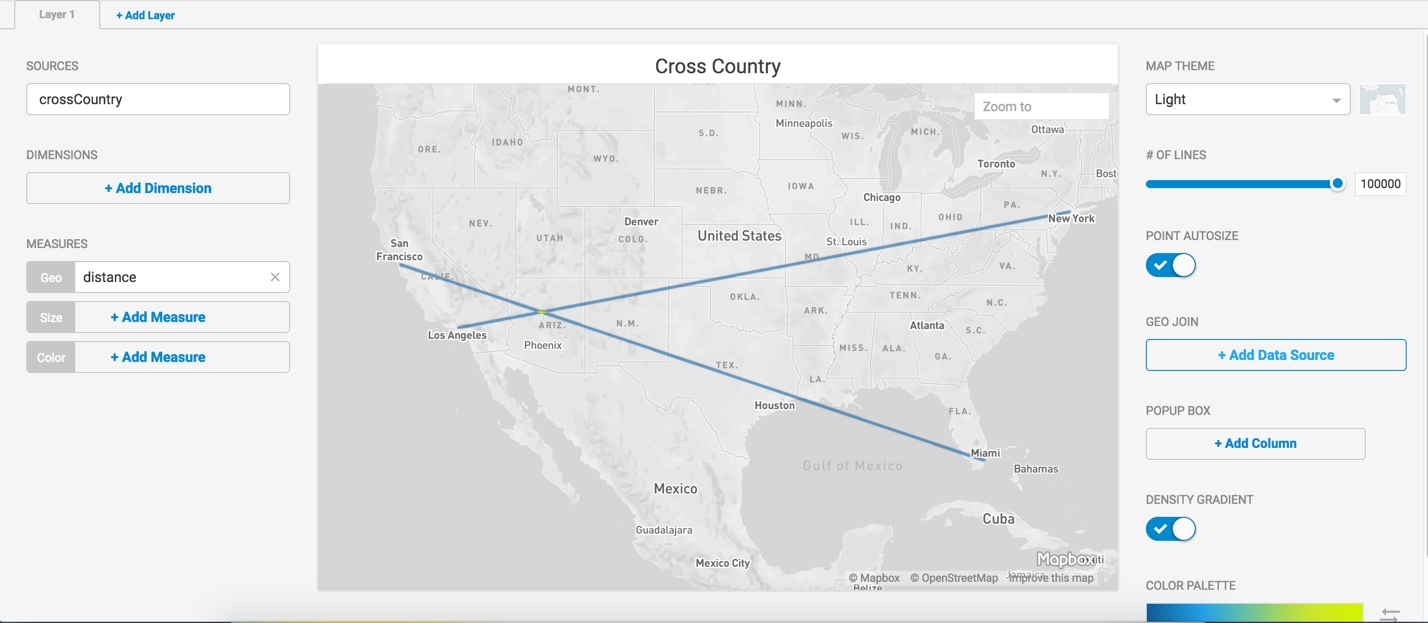
For example, you can import this CSV file with coordinates for Los Angeles to New York, San Francisco to Miami.
Save the following content as
crossCountry.csv.cities,distance "LA-NY","LINESTRING( -118.2437 34.0522, -74.0060 40.7128)" "SF-MI","LINESTRING( -122.4194 37.7749, -80.1918 25.7617)"Open Immerse
Choose the Data Manager tab.
Click Import Data.
Click Import data from a local file.
Click the + icon to browse for and open your file.
Click Preview.
Name the table crossCountry.
Verify the data is correct and click Import Table.
Click the Dashboards tab.
Click New Dashboard.
Click Add Chart.
Choose Linemap.
Click + Add Data Source.
Choose crossCountry as the data source.
In the Geo field, click + Add Measure.
Choose Distance.
Your Linemap links Los Angeles to New York, San Francisco to Miami.
Zoom
You can zoom in and out of a Linemap chart in the following ways:
Using the mouse scrolling wheel.
Selecting an area by holding down the Shift key and using the mouse to select the zoom area.
Using the Zoom To box in the upper right of the map:
Type the name of a geographic location (address, city, state, or country) and optional zoom level. For example, Denver, CO, !8 zooms to Denver, Colorado, with a zoom level of 8.
Enter latitude and longitude coordinates, and optional zoom level. For example, 39.26911, -76.54068, !9 takes you to Baltimore, MD, at zoom level 9.
Last updated