Pie
To learn more about pie charts and how to create one, please view this video.
The Pie chart lets you compare the relative sizes of groups of data as segments of a circle.
Features
Quantity
Notes
Use a Pie chart to show the relative proportions of a small number categories. If you have many categories, or the values are very similar in size, a Bar chart is often a more effective way to compare the categories. Note also that you should not create Pie charts with a mix of positive and negative values.
Chart Style
You can style your chart as a Donut or a Pie, depending on your dessert preference. The default Donut style tends to make it easier to see the relative sizes of the chart divisions.
Sort By
SORT BY determines the order of the sections starting at the 12 o'clock position and proceeding around the chart in clockwise fashion.
# of Groups
You can divide your chart into up to 100 values. A smaller number of values often results in a more readable chart.
Null Dimensions
You have the option of hiding null dimensions if they are not significant in your data sample.
Color Palette
You can choose 1, 2, 3, 4, or 9 colors for your chart. You can also use a gradient color to show relative values within a dimension.
Labels
You can toggle off or on the absolute value labels on the pie sections. This toggle is always enabled and available.
When the measure values for your chart represent the number of records or a sum aggregate value, you can show percentage labels of each slice relative to the other slices of the pie. This value always appears in the popup when you hover over a slice (when the feature is available). In the chart editor, you can toggle the percentages on or off (default) for each slice.
If you create the chart using Number of Records or the Sum size measure, then change to a different kind of value, the Percentage and "All Others" settings toggles turn off, with a ToolTip explanation when you hover over them.
Custom Measure Formatting
You can also use custom measure formats for the value in your chart. See Customizing Measure and Date Formats.
"All Others" Value
When you select "All Others," you add an extra section to the pie representing all dimension groups that are not already represented by a slice. The section is grey and cannot be selected to crossfilter. Otherwise, it acts like any other slice. You can toggle the All Others value on (default) or off in the chart editor.
Pie Chart Examples
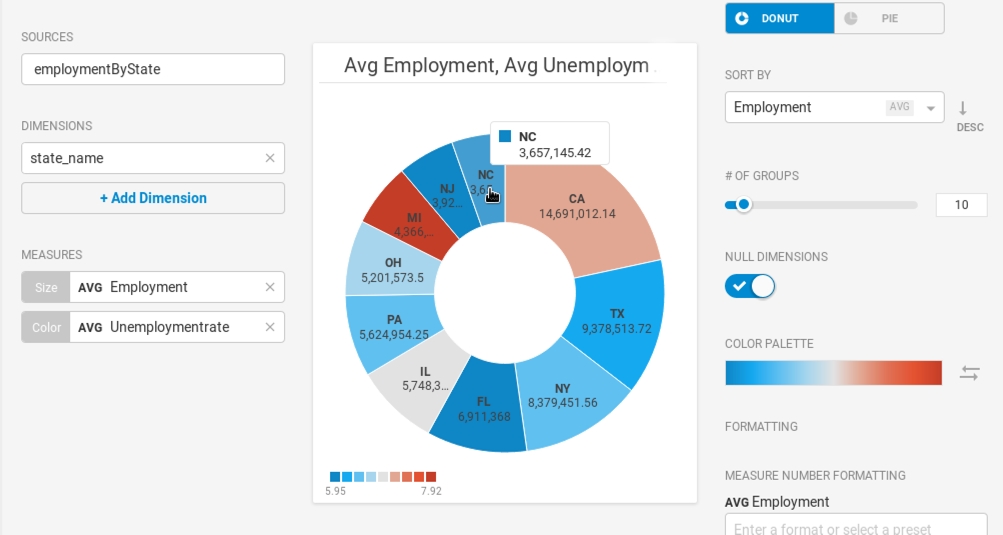
Create a new Pie chart. Choose a Data Source. This example graphs employment statistics for all 50 United States for the year 1980. The data is available at the University of Kentucky website.
Use the Dimension state_name and the Size measure AVG Employment.
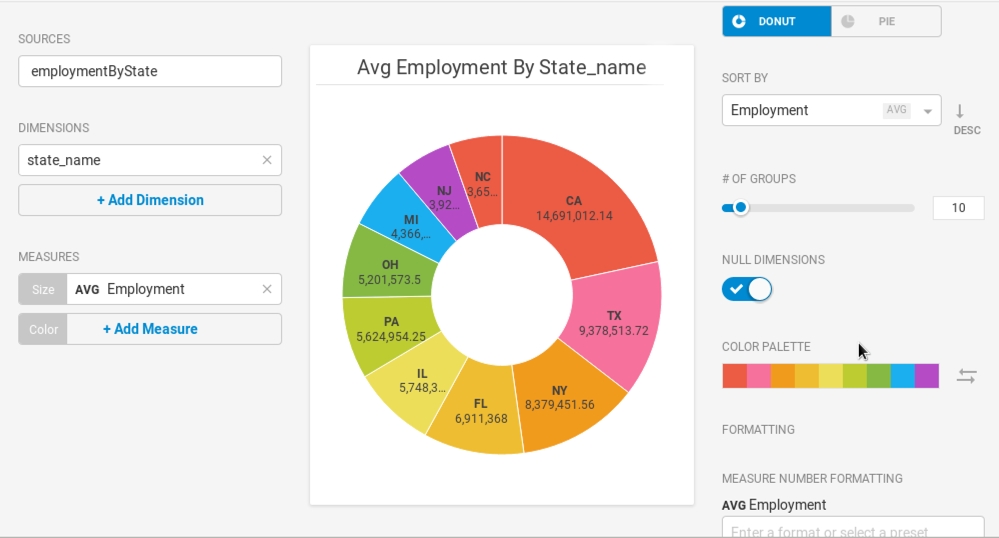
You can use the Color measure to reflect the Unemployment_rate, providing more nuanced understanding of the relative segments.
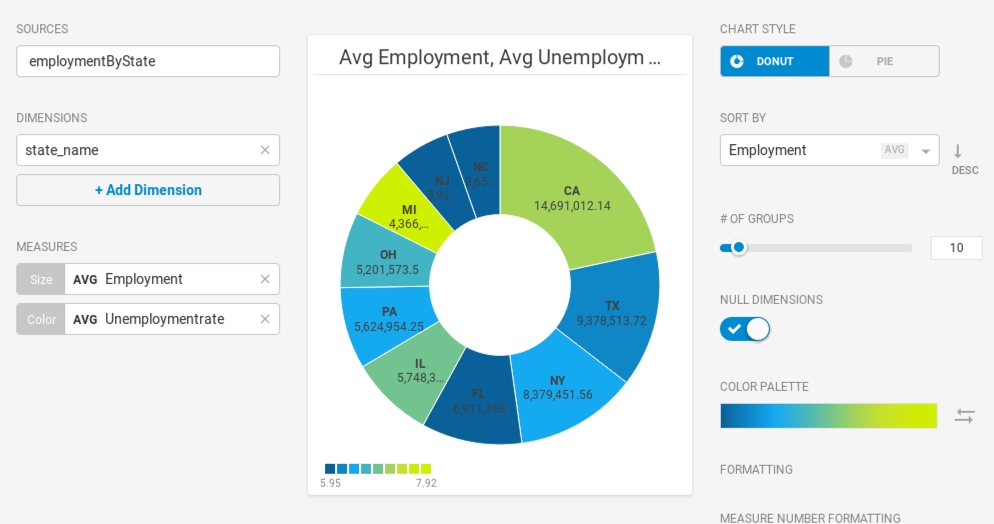
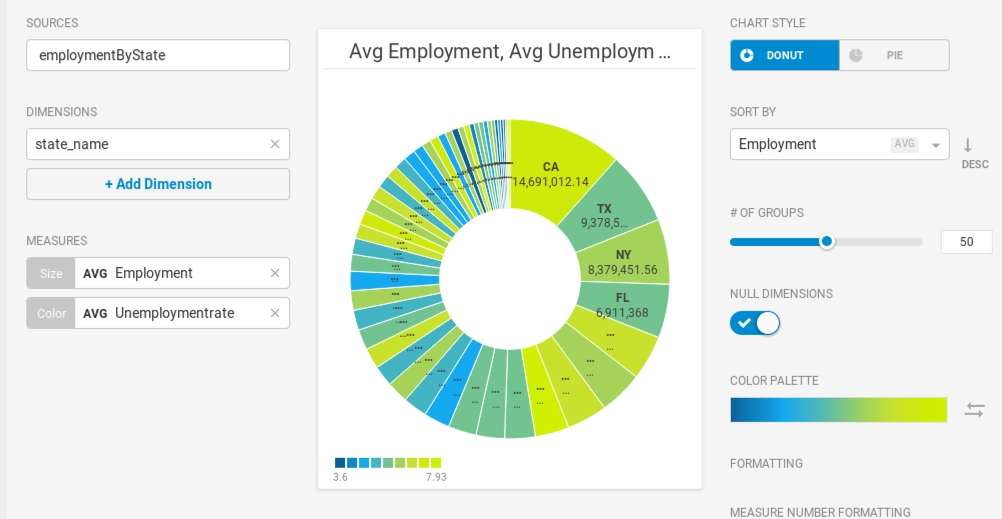
There are 50 states, so it might be tempting to show all 50 in the chart. The problem becomes obvious when there are too many segments with too little variation to provide meaningful analysis. 10 or fewer is probably a reasonable setting for # of Groups.
Changing the Color Palette might make an outlier such as Michigan stand out more effectively.
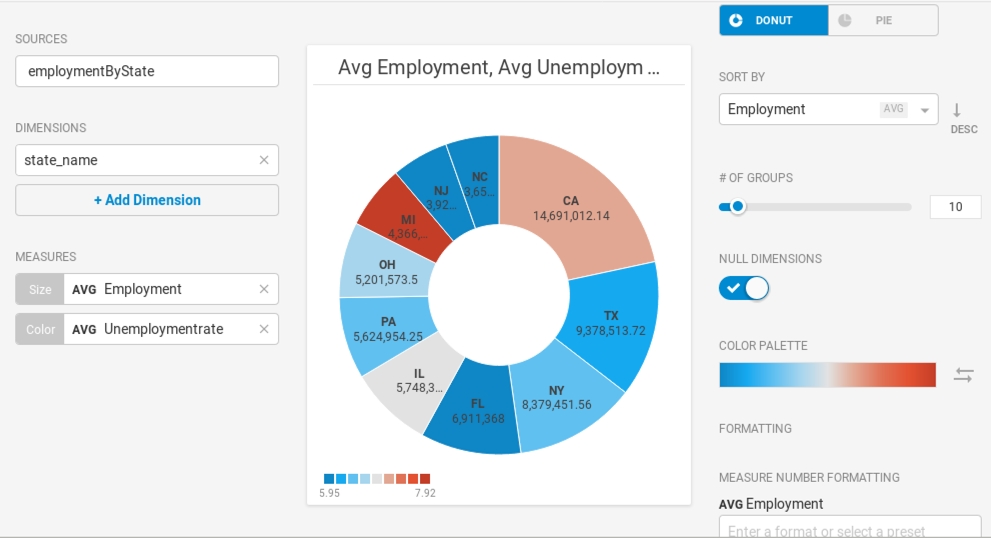
Where the segments do not have sufficient width to display the measures, you can mouse over to see a pop-up with the information for your chosen segment.
Last updated