Getting More from Your Data
Source code can be found at the end of this tutorial.
This tutorial builds on the Getting Started with Vega tutorial by color-coding tweets according to language:
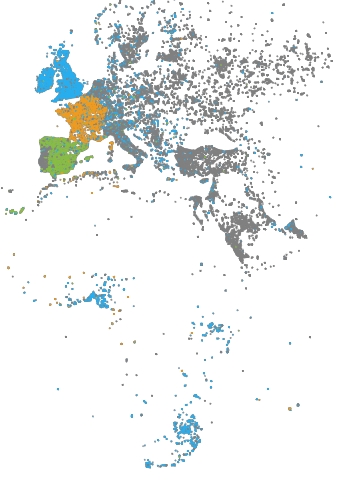
Tweets in English are blue.
Tweets in French are orange.
Tweets in Spanish are green.
All other tweets are light or dark gray.
To highlight language in the visualization, the example specifies the language column query in the Vega data property, and associates language with color.
"data:" [
{
"name": "tweets",
"sql": "SELECT goog_x as x, goog_y as y, lang as color, tweets_nov_feb.rowid FROM tweets_nov_feb"
}The Scales property maps the language abbreviation string to a color value. Because we want to map discrete domain values to discrete range values, we specify a color scale with an ordinal type scale:
"scales:" [
.
.
.
{
"name": "color",
"type": "ordinal",
"domain": ["en", "es", "fr"],
"range": ["#27aeef", "#87bc45", "#ef9b20"],
"default": "gray",
"nullValue": "#cacaca"
}
]You can specify a default color values for values not specified in range and for data items with a value of null. In this example, tweets in languages other than English, Spanish, or French are colored gray and tweets with a language value of null are colored light gray (#cacaca).
Similar to using x and y scales to map Marks property x and y fields to the visualization area, you can scale the fillColor property to the visualization area.
In previous examples the fill color of points representing tweets was statically specified as blue:
"marks:" [
{
"type:" "points",
"from:" {
"data:" "tweets"
},
"properties:" {
.
.
.
},
"fillColor": "blue",
"size:" {"value:" 3}
}
}
]This example, uses Value Reference to specify the fill color:
"marks:" [
{
"type:" "points",
"from:" {
"data:" "tweets"
},
"properties:" {
.
.
.
},
"fillColor:" {
"scale": "color",
"field": "color"
},
"size:" 3
}
}
]The fillColor references the color scale and performs a lookup on the current language value, from the color data table field.
Source Code
Getting More Insight Tutorial Directory Structure
index.html
/js
browser-connector.js
vegaspec.js
vegademo.jsHTML
Getting More Insight Tutorial index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>OmniSci</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<script src="js/browser-connector.js"></script>
<script src="js/vegaspec.js"></script>
<script src="js/vegademo.js"></script>
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', init, false);
</script>
</body>
</html>JavaScript
Getting More Insight Tutorial vegademo.js
function init() {
var vegaOptions = {}
var connector = new MapdCon()
.protocol("http")
.host("my.host.com")
.port("6273")
.dbName("omnisci")
.user("omnisci")
.password("changeme")
.connect(function(error, con) {
con.renderVega(1, JSON.stringify(exampleVega), vegaOptions, function(error, result) {
if (error) {
console.log(error.message);
}
else {
var blobUrl = `data:image/png;base64,${result.image}`
var body = document.querySelector('body')
var vegaImg = new Image()
vegaImg.src = blobUrl
body.append(vegaImg)
}
});
});
}Getting More Insight Tutorial vegaspec.js
const exampleVega = {
"width": 384,
"height": 564,
"data": [
{
"name": "tweets",
"sql": "SELECT goog_x as x, goog_y as y, lang as color, tweets_data_table.rowid FROM tweets_data_table"
}
],
"scales": [
{
"name": "x",
"type": "linear",
"domain": [
-3650484.1235206556,
7413325.514451755
],
"range": "width"
},
{
"name": "y",
"type": "linear",
"domain": [
-5778161.9183506705,
10471808.487466192
],
"range": "height"
},
{
"name": "color",
"type": "ordinal",
"domain": ["en", "es", "fr"],
"range": ["#27aeef", "#87bc45", "#ef9b20"],
"default": "gray",
"nullValue": "#cacaca"
}
],
"marks": [
{
"type": "points",
"from": {
"data": "tweets"
},
"properties": {
"x": {
"scale": "x",
"field": "x"
},
"y": {
"scale": "y",
"field": "y"
},
"fillColor": {
"scale": "color",
"field": "color"
},
"size": 3
}
}
]
};