Installing on Ubuntu
In this section, you will find recipes to install HEAVY.AI platform and NVIDIA drivers using package manager like apt or tarball.
HEAVY.AI Installation on Ubuntu
This is an end-to-end recipe for installing HEAVY.AI on a Ubuntu 22.04 machine using CPU and GPU devices.
The order of these instructions is significant. To avoid problems, install each component in the order presented.
Assumptions
These instructions assume the following:
You are installing on a “clean” Ubuntu 22.04 host machine with only the operating system installed.
Your HEAVY.AI host only runs the daemons and services required to support HEAVY.AI.
Your HEAVY.AI host is connected to the Internet.
Preparation
Prepare your Ubuntu machine by updating your system, creating the HEAVY.AI user (named heavyai), installing kernel headers, installing CUDA drivers, and optionally enabling the firewall.
Update and Reboot
Update the entire system:
2. Install the utilities needed to create Heavy.ai repositories and download archives:
3. Install the headless JDK and the utility apt-transport-https:
4. Reboot to activate the latest kernel:
Create the HEAVY.AI User
Create a group called heavyai and a user named heavyai, who will be the owner of the HEAVY.AI software and data on the filesystem.
Create the group, user, and home directory using the
useraddcommand with the--user-groupand--create-homeswitches.
2. Set a password for the user:
3. Log in with the newly created user:
Installation
Install the HEAVY.AI using APT and a tarball.
Install NVIDIA Drivers ᴳᴾᵁ ᴼᴾᵀᴵᴼᴺ
If your system uses NVIDIA GPUs, but the drivers not installed, install them now. See Install NVIDIA Drivers and Vulkan on Ubuntu for details.
Installing with APT
Download and add a GPG key to APT.
Add a source apt depending on the edition (Enterprise, Free, or Open Source) and execution device (GPU or CPU) you are going to use.
Use apt to install the latest version of HEAVY.AI.
Installing with a Tarball
First create the installation directory.
Download the archive and install the software. A different archive is downloaded depending on the Edition (Enterprise, Free, or Open Source) and the device used for runtime (GPU or CPU).
Configuration
Follow these steps to prepare your HEAVY.AI environment.
Set Environment Variables
For convenience, you can update .bashrc with these environment variables
Although this step is optional, you will find references to the HEAVYAI_BASE and HEAVYAI_PATH variables. These variables contain respectively the paths where configuration, license, and data files are stored and where the software is installed. Setting them is strongly recommended.
Initialization
Run the systemd installer to create heavyai services, a minimal config file, and initialize the data storage.
Accept the default values provided or make changes as needed.
The script creates a data directory in $HEAVYAI_BASE/storage (default /var/lib/heavyai/storage) with the directories catalogs, data, export and log.The import directory is created when you insert data the first time. If you are HEAVY.AI administrator, the log directory is of particular interest.
Activation
Start and use HeavyDB and Heavy Immerse. ¹
Heavy Immerse is not available in the OSS Edition, so if running the OSS Edition the systemctl command using the heavy_web_server has no effect.
Enable the automatic startup of the service at reboot and start the HEAVY.AI services.
Configure Firewall ᴼᴾᵀᴵᴼᴺᴬᴸ
If a firewall is not already installed and you want to harden your system, install theufw.
To use Heavy Immerse or other third-party tools, you must prepare your host machine to accept incoming HTTP(S) connections. Configure your firewall for external access.
For more information, see https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/firewall.html.
Licensing HEAVY.AI ᵉᵉ⁻ᶠʳᵉᵉ ᵒⁿˡʸ
If you are using Enterprise or Free Edition, you need to validate your HEAVY.AI instance with your license key.
Skip this section if you are on Open Source Edition ²
Copy your license key of Enterprise or Free Edition from the registration email message. If you do not have a license and you want to evaluate HEAVI.AI in an unlimited
enterprise environment, contact your Sales Representative or register for your 30-day trial of Enterprise Edition here. If you need a Free License you can get one here.
Connect to Heavy Immerse using a web browser connected to your host machine on port 6273. For example,
http://heavyai.mycompany.com:6273.When prompted, paste your license key in the text box and click Apply.
Log into Heavy Immerse by entering the default username (
admin) and password (HyperInteractive), and then click Connect..
Final Checks
To verify that everything is working, load some sample data, perform a heavysql query, and generate a Pointmap using Heavy Immerse ¹
Load Sample Data and Run a Simple Query
HEAVY.AI ships with two sample datasets of airline flight information collected in 2008, and a census of New York City trees. To install sample data, run the following command.
Connect to HeavyDB by entering the following command in a terminal on the host machine (default password is HyperInteractive):
Enter a SQL query such as the following
The results should be similar to the results below.
Create a Dashboard Using Heavy Immerse ᵉᵉ⁻ᶠʳᵉᵉ ᵒⁿˡʸ ¹
After installing Enterprise or Free Edition, check if Heavy Immerse is running as intended.
Connect to Heavy Immerse using a web browser connected to your host machine on port 6273. For example,
http://heavyai.mycompany.com:6273.Log into Heavy Immerse by entering the default username (
admin) and password (HyperInteractive), and then click Connect.
Create a new dashboard and a Scatter Plot to verify that backend rendering is working.
Click New Dashboard.
Click Add Chart.
Click SCATTER.
Click Add Data Source.
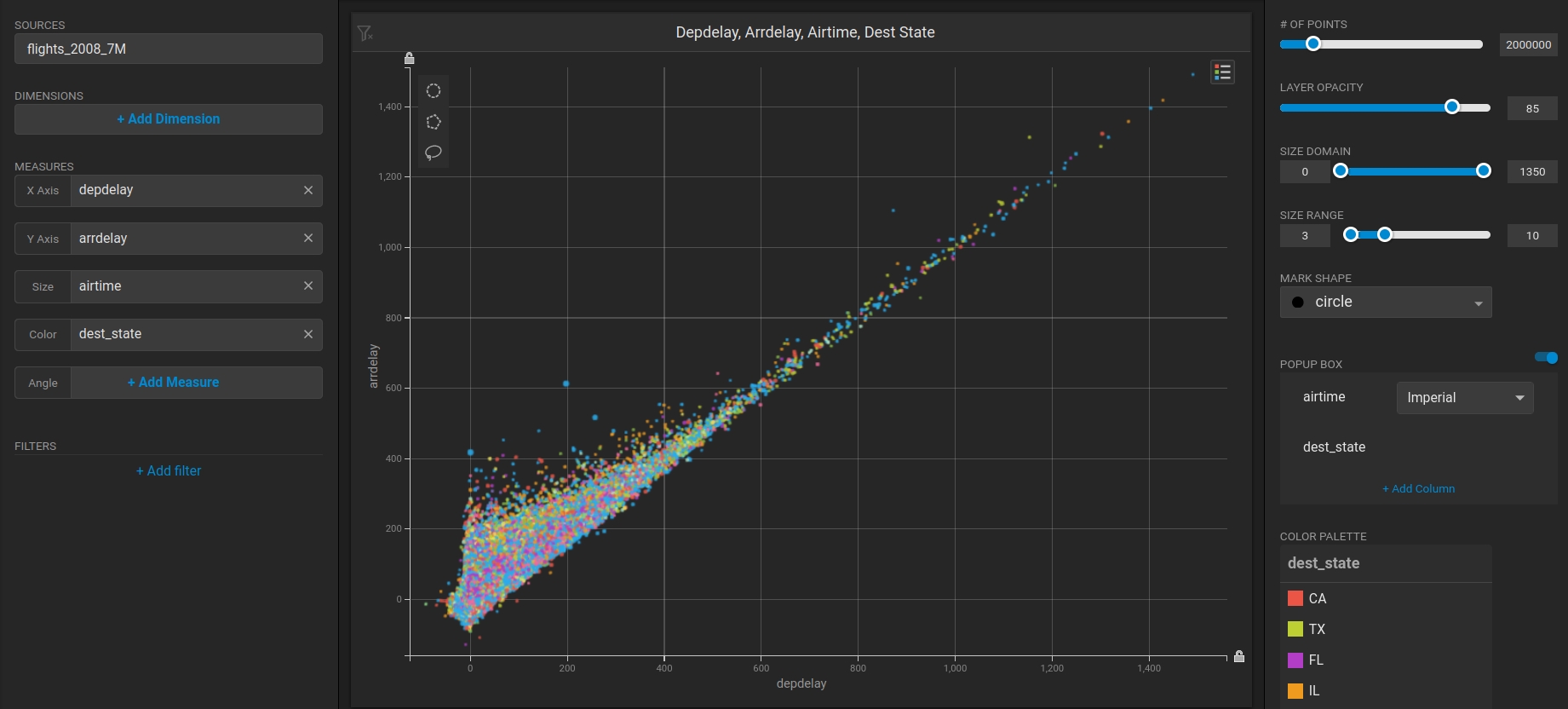
Choose the flights_2008_10k table as the data source.
Click X Axis +Add Measure.
Choose depdelay.
Click Y Axis +Add Measure.
Choose arrdelay.
Click Size +Add Measure.
Choose airtime.
Click Color +Add Measure.
Choose dest_state.
The resulting chart shows, unsurprisingly, that there is a correlation between departure delay and arrival delay.
Create a new dashboard and a Table chart to verify that Heavy Immerse is working.
Click New Dashboard.
Click Add Chart.
Click Bubble.
Click Select Data Source.
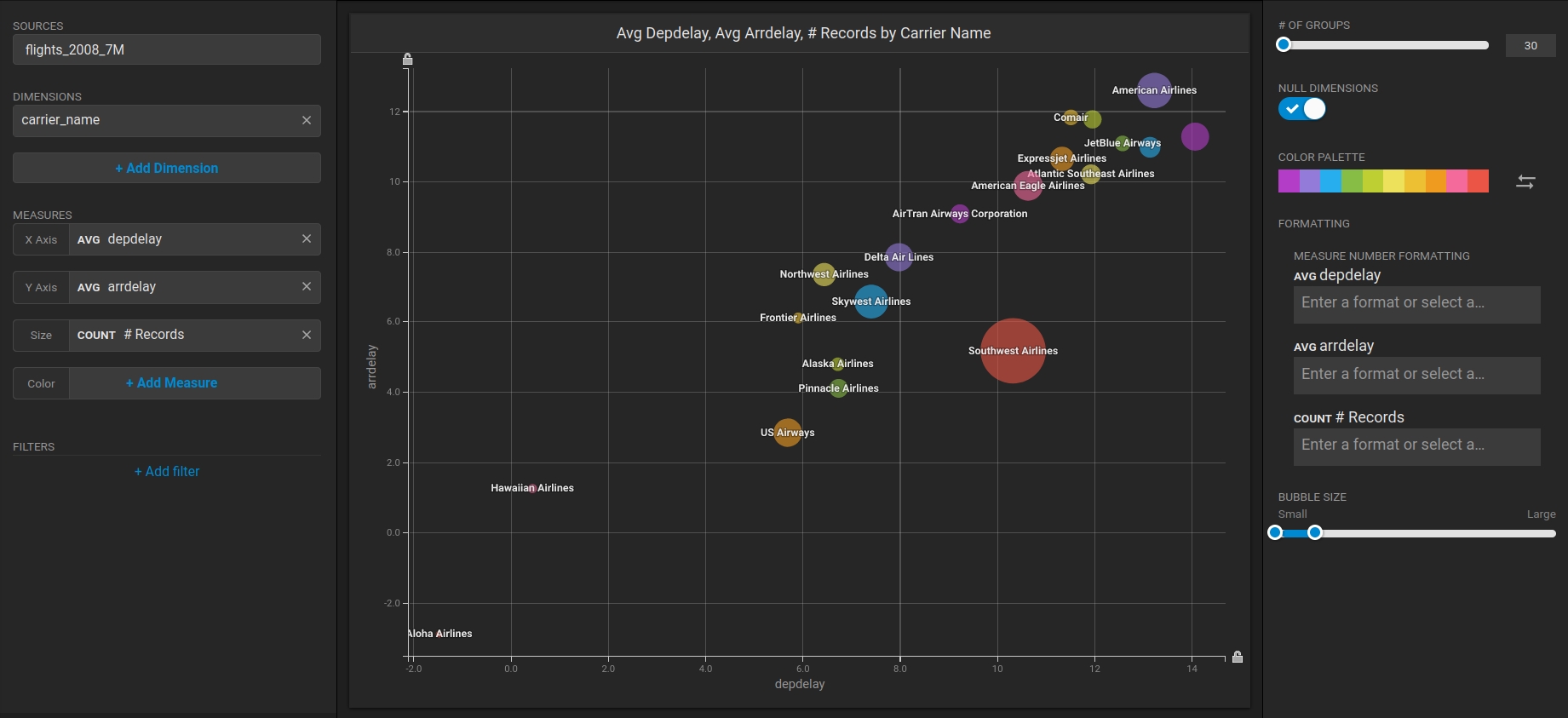
Choose the flights_2008_10k table as the data source.
Click Add Dimension.
Choose carrier_name.
Click Add Measure.
Choose depdelay.
Click Add Measure.
Choose arrdelay.
Click Add Measure.
Choose #Records.
The resulting chart shows, unsurprisingly, that also the average departure delay is correlated to the average of arrival delay, while there is quite a difference between Carriers.
¹ In the OS Edition, Heavy Immerse is unavailable.
² The OS Edition does not require a license key.
Install NVIDIA Drivers and Vulkan on Ubuntu
Installation Prerequisites
Hardware Check
Check that your system has a compatible NVIDIA GPU. If you don't know the exact GPU model in your system run this command:
This command should output one row per installed NVIDIA GPU. Check that your hardware is compatible on our Hardware Requirements page. Note that you can still install the CPU Edition of HEAVY.AI on machines that do not have an NVIDIA GPU.
Pre-Installation Updates
Upgrade the system and the kernel, then the machine if needed.
Install Kernel Headers
Install kernel headers and development packages.
Install the extra packages.
Installing Vulkan Library
The rendering engine of HEAVY.AI (present in Enterprise Editions) requires a Vulkan-enabled driver and the Vulkan library. Without these components, the database itself may not be able to start.
Install the Vulkan library and its dependencies using apt.
For more information about troubleshooting Vulkan, see the Vulkan Renderer section.
Installing NVIDIA Drivers
Installing NVIDIA drivers with support for the CUDA platform is required to run GPU-enabled versions of HEAVY.AI.
Each version of HEAVY.AI has a minimum required driver version, which is documented in the Software Requirements page. You can generally install NVIDIA drivers newer than the minimum required version, but the version listed in our Software Requirements page reflects the NVIDIA driver used for software testing.
You can install NVIDIA drivers in multiple ways, we've outlined three available options below - we recommend Option 1.
Option 1: Install NVIDIA drivers with CUDA toolkit from NVIDIA Website
Option 2: Install NVIDIA drivers via .run file using the NVIDIA Website
Option 3: Install NVIDIA drivers using APT package manager
What is CUDA? What is the CUDA toolkit?
CUDA is a parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model. It uses a CUDA-enabled graphics processing unit (GPU) for general-purpose processing. The CUDA platform provides direct access to the GPU virtual instruction set and parallel computation elements. For more information on CUDA unrelated to installing HEAVY.AI, see https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-zone.
The CUDA Toolkit from NVIDIA provides everything you need to develop GPU-accelerated applications. The CUDA Toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, a compiler, development tools and the CUDA runtime. The CUDA Toolkit is not required to run HEAVY.AI, but you must install the CUDA toolkit if you use advanced features like C++ User-Defined Functions and or User-Defined Table Functions to extend the database capabilities.
Option 1: Install NVIDIA Drivers with CUDA Toolkit from NVIDIA Website
Open https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit-archive and select the desired CUDA Toolkit version to install.
In the "Target Platform" section, follow these steps:
For "Operating System" select Linux
For Architecture" select x86_64
For "Distribution" select Ubuntu
For "Version" select the version of your operating system (20.04)
For "Installer Type" choose deb (network) **
One by one, run the presented commands in the Installer Instructions section on your server.
Option 2: Install NVIDIA Drivers via .run file using the NVIDIA Website
Install the CUDA package for your platform and operating system according to the instructions on the NVIDIA website (https://www.nvidia.com/download/index.aspx).
If you don't know the exact GPU model in your system run this command
You'll get an output in the format Product Type, Series and Model
In this example, the Product type is Tesla the Series is T (as Turing), and the model is T4.
Select the Product Type as the one you got with the command.
Select the correct Product Series and Product Type for your installation.
In the Operating System dropdown list, select Linux 64-bit.
In the CUDA Toolkit dropdown list, click a supported version (11.4 or higher).
Click Search.
On the resulting page, verify the download information and click Download
On the subsequent page, if you agree to the terms, right click on "Agree and Download" and select "Copy Link Address". You may also manually download and transfer to your server, skipping the next step.
On your server, type
wgetand paste the URL you copied in the previous step. Press enter to download.
Install the tools needed for installation.
Change the permissions of the downloaded .run file to allow execution, and run the installation.
Option 3: Install NVIDIA drivers using APT
Install a specific version of the driver for your GPU by installing the NVIDIA repository and using the apt package manager.
Run the command to get a list of the available driver's version
Install the driver version needed with apt
NVIDIA Driver Post-Installation steps
Reboot your system to ensure the new version of the driver is loaded
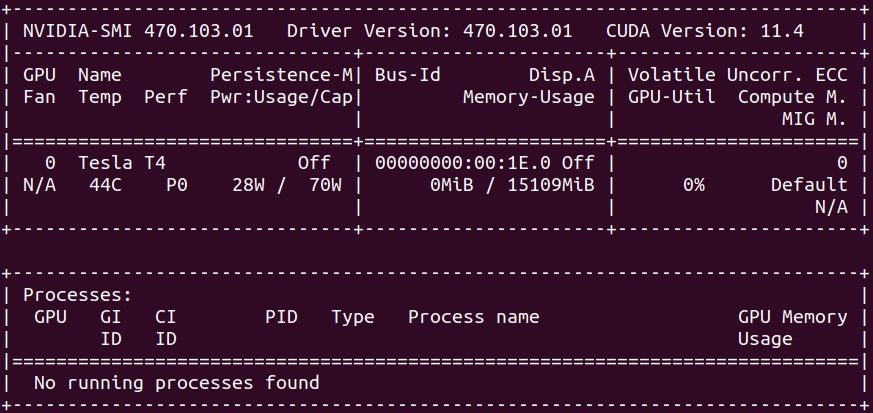
Verify Successful NVIDIA driver installation
Run nvidia-smi to verify that your drivers are installed correctly and recognize the GPUs in your environment. Depending on your environment, you should see something like this to confirm that your NVIDIA GPUs and drivers are present.
Install Vulkan library
The rendering engine of HEAVY.AI requires a Vulkan-enabled driver and the Vulkan library. Without these components, the database itself can't even start without disabling the back-end renderer.
Install the Vulkan library and its dependencies using apt.
For more information about troubleshooting Vulkan, see the Vulkan Renderer section.
Advanced Installation
You must install the CUDA toolkit and Clang if you use advanced features like C++ User-Defined Functions and or User-Defined Table Functions to extend the database capabilities.
Install CUDA Toolkit ᴼᴾᵀᴵᴼᴺᴬᴸ
If you installed NVIDIA drivers using Option 1 above, the CUDA toolkit is already installed; you may proceed to the verification step below.
Install the NVIDIA public repository GPG key.
Add the repository.
List the available Cuda toolkit versions.
Install the CUDA toolkit using apt.
Verification
Check that everything is working and the toolkit has been installed.
Install Clang ᴼᴾᵀᴵᴼᴺᴬᴸ
You must install Clang if you use advanced features like C++ User-Defined Functions and or User-Defined Table Functions to extend the database capabilities. Install Clang and LLVM dependencies using apt.
Verification
Check that the software is installed and in the execution path.
For more information, see C++ User-Defined Functions.